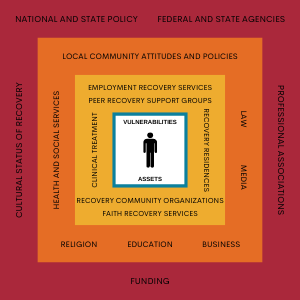
Recovery Oriented Systems of Care
RECOVERY ORIENTED SYSTEMS OF CARE (ROSC) is an organizing paradigm for addressing substance use disorders through a supportive network of individual and societal factors.
We use a recovery-oriented systems of care model to illustrate the numerous factors that directly and indirectly affect ones recovery from a substance use disorder.
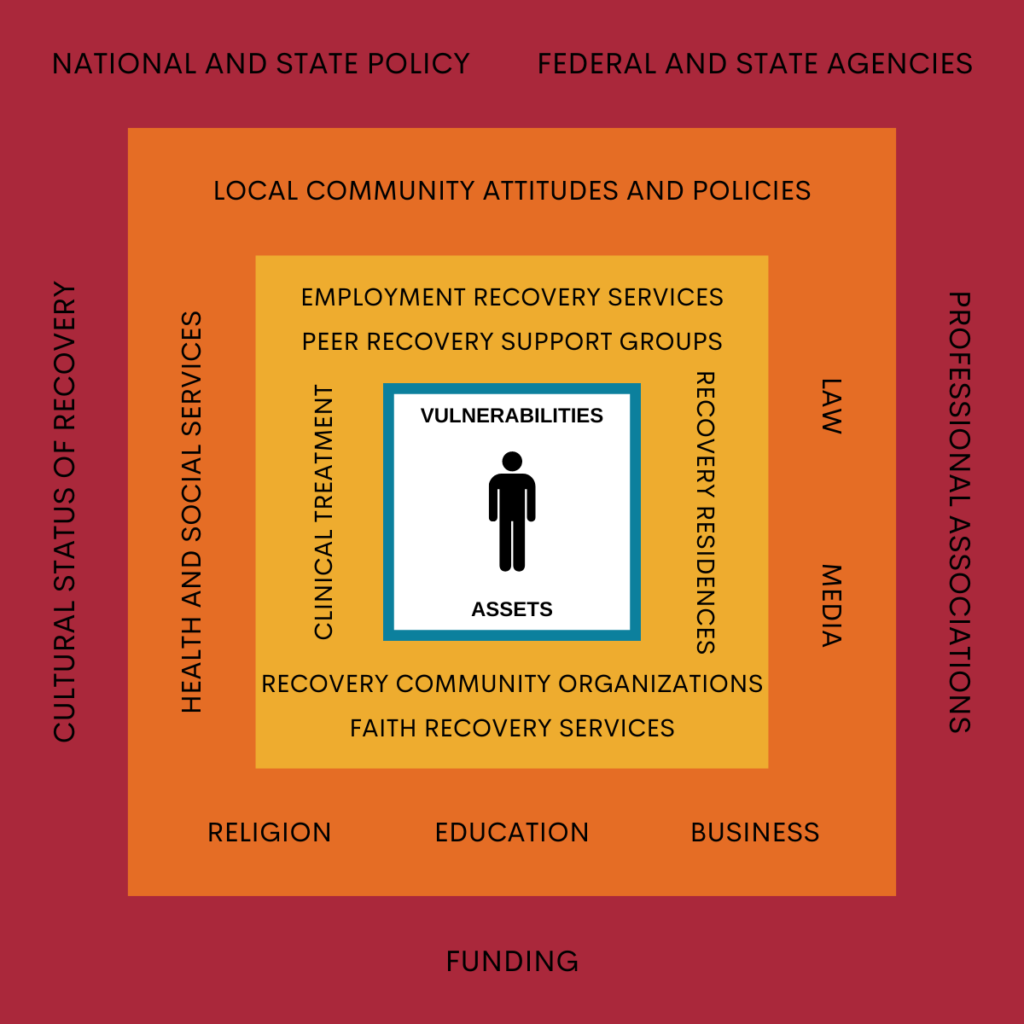
Below we explore the different recovery systems of care, beginning with the factors that affect individual recovery most directly, moving to the factors and institutions that tend to have an increasingly indirect affect on the recovery of an individual.
INDIVIDUAL FACTORS AFFECTING RECOVERY
- ASSETS
-
Attributes that an individual possesses, that act to help or support recovery (e.g. attitudes, beliefs, intentions, biology, etc.).
- VULNERABILITIES
-
Attributes that an individual possesses, that act to obstruct or hinder recovery (e.g. attitudes, beliefs, intentions, biology, etc.).
FACTORS AFFECTING RECOVERY MOST DIRECTLY
- FAMILY
-
Family members can play a key role in trying to motivate and encourage a loved one to seek help, through education and pre-planning, intervention, contingency management, and as a means of support in sobriety.
Additional resources for loved ones are presented on our Resources for Loved Ones page.
- CULTURE
-
The cultural outlook on addiction and substance use has changed dramatically over the past decade. Organizations from grassroots to federal have worked hard to fight the stigmatization of addiction and change public opinion of substance use disorders.
Culture might also entail the attitudes, morals, and religious beliefs of the individuals and families affected.
- NEIGHBORHOOD
-
The neighborhoods and communities in which we live in can affect ones ability to recover from substance use. Having a higher number of liquor stores nearby can be a barrier to recovery, while having resources such as a needle exchange program or an addiction treatment center can help support recovery.
- SOCIAL CIRCLE
-
Developing a network of like-minded individuals can help individuals in early recovery remain motivated to stay abstinent. Throughout the course of treatment, clinicians, recovery coaches, and even support groups will all highlight the importance of surrounding oneself with other people in recovery. Those who surround themselves with other people in recovery are more likely to remain in recovery.
FACTORS AFFECTING RECOVERY SOMEWHAT DIRECTLY
- MULTIPLE PATHWAYS TO RECOVERY
-
Employment, peer-recovery, recovery residences, clinical treatment, recovery community organizations (e.g. recovery community centers), and faith-based recovery services are presented in detail on our multiple pathways to recovery page.
FACTORS AFFECTING RECOVERY SOMEWHAT INDIRECTLY
- EDUCATION
-
Accessibility to GED and university level programs incentivize and support recovery, reintegrating individuals back into mainstream society.
- LOCAL COMMUNITY ATTITUDES & POLICIES
-
There is a well-reported attitude often referred to as NIMBY (not in my back yard), which is related to community residents’ resistance to adopt various addiction and health-related initiatives in their neighborhood due to concerns about what the initiative will bring. Research has revealed that many concerns around increases in crime rates surrounding addiction treatment centers are unfounded.
- MEDIA
-
The ways in which the media and mainstream press write, talk, and portray substance use disorders matters, especially in highly stigmatized conditions such as substance use disorder.
- HEALTH & SOCIAL SERVICES
-
Organizations big and small, and funded from a variety of federal and individual sources, provide support to individuals and families affected by substance use disorder, connecting individuals with treatment and community resources.
- BUSINESS
-
Larger business practices of hiring individuals that may have a CORI form (criminal offender record information) or criminal record from prior alcohol or drug-related offenses, policies and investments in Employee Assistance Program (EAP) resources, corporate giving practices, and community re-investment can all help to impact recovery.
Read blog on the impact of Addiction in the Workplace
- RELIGION
-
Religion comprises the religious beliefs toward substance use disorder, and the support of religious communities in supporting those in recovery.
Read more on Faith-based Recovery Services
- LAW
-
Individual laws affect everything from individual sentencing to prescribing patterns and the licensing of physicians. Individual laws are often affected or determined by national and state level policies, described in more detail in the section below.
Read blog on Drug Policy in the United States
FACTORS AFFECTING RECOVERY MOST INDIRECTLY
- NATIONAL & STATE POLICY
-
National and state policies and regulation are put in place to help protect citizens. Alcohol and drug policy is the summation of related-laws, and affects thing such as:
- Legalization and medicalization of marijuana or other particular substances
- The availability of drug courts and policy enforcement by the criminal justice system
- Physician prescribing and reporting practices
- Healthcare regulation and insurance coverage
- Funding allocations for research and resources
Read blog on Drug Policy in the United States
- FUNDING
-
Funding can come from individual donors, corporate philanthropy, private foundations, or government institutions.
Government funding of alcohol and drug addiction research is reported to be:
- $2,188,000,000 in 2016
- Funding is estimated to decrease to $1,753,000,000 in 2018
Compared to 2016 federal funding of other chronic conditions:
- Heart and Cardiovascular Disease: $3,598,000,000
- Cancer: $9,212,000,000
- Diabetes: $1,084,000,000
- PROFESSIONAL ASSOCIATIONS
-
Professional associations are often leaders in accreditation, scientific research and advocacy for recovery-oriented treatment and programs.
Central Addiction-related Professional Associations include:
- American Psychological Association (APA)
- American Psychiatric Association
- American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM)
- FEDERAL & STATE AGENCIES
-
Similar to associations like APA and ASAM, federal and state agencies are funded by American tax dollars, and serve to carry out the laws and policies of the other branches of government through regulation, enforcement, and education among other things.
Central Addiction-related Federal Agencies include:
- NIDA (NIH): National Institute on Drug Abuse
- SAMHSA: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Administration
- NIAAA: National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism
- CDC: Centers for Disease Control
- DEA: Drug Enforcement Administration
- FDA: Food and Drug Administration
- CULTURAL STATUS OF RECOVERY
-
Over 23 million Americans aged 12 or older have a substance use disorder, but only about 10% of these individuals receive adequate treatment. At least in part, this shortfall in accessing treatment may be due to the cultural stigma surrounding addiction that stems from a long history of religious influence equating heavy use of certain substances (e.g., becoming intoxicated on alcohol) or any use of a non-socially sanctioned illicit substance (e.g., cocaine, marijuana), with self-indulgence, sin, moral defects, or individual weakness.
While such cultural stigma against becoming intoxicated or using illicit substances are associated with reductions in substance use behavior, for those that become addicted to the substance (legal or illegal) this same stigma can increase shame and secrecy and decrease disclosure of a problem and help-seeking


